There are numerous factors that are used to calculate your home insurance rate. Some of these are obvious, like brick vs frame, age of the roof, and when the home was built. But there are other less obvious characteristics that can affect your rate, and in some instances, your eligibility.
Types of Acceptable Heat
Electric heat (heat pumps, electric baseboard) and gas furnaces (natural and propane) are generally acceptable heating types as long as they’ve been updated and/or serviced within the guidelines provided by your carrier.
Underground fuel tanks (ex. oil tanks) are generally not acceptable for home insurance. It does not matter if the tank is used or not. Some carriers will accept underground tanks so it’s important to check your carriers’ underwriting guidelines for acceptability.
Wood stoves are acceptable in certain scenarios. Again, you’ll want to check with your carrier about acceptability for wood stoves and inserts. One item to note about wood stoves is that they cannot be the main heat source—this is generally unacceptable by the majority of insurance carriers.
What if your property has no heat? Then your property will not be acceptable for the majority of carriers. While specific wording varies from carrier to carrier, a thermostatically controlled heat source is a requirement for homeowners insurance.
Most homes use one of these primary heat sources:
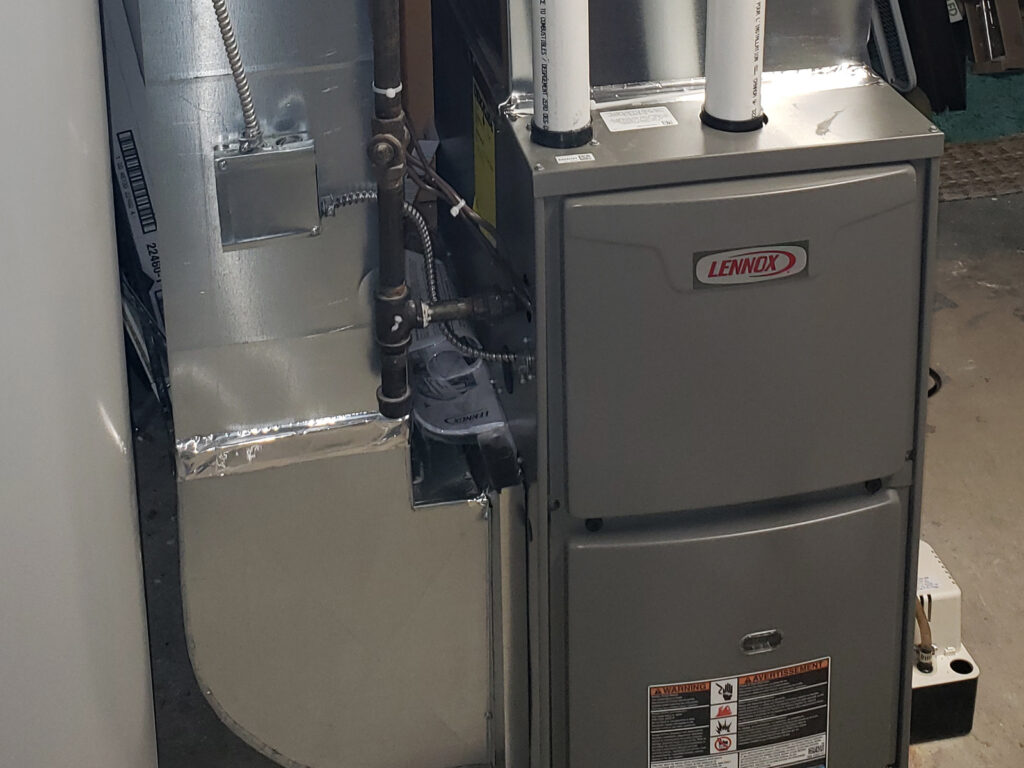
- Furnace: These heating systems use natural gas, propane, oil, electricity or a combination of fuels to create warm air that’s distributed through your home using ductwork and vents.

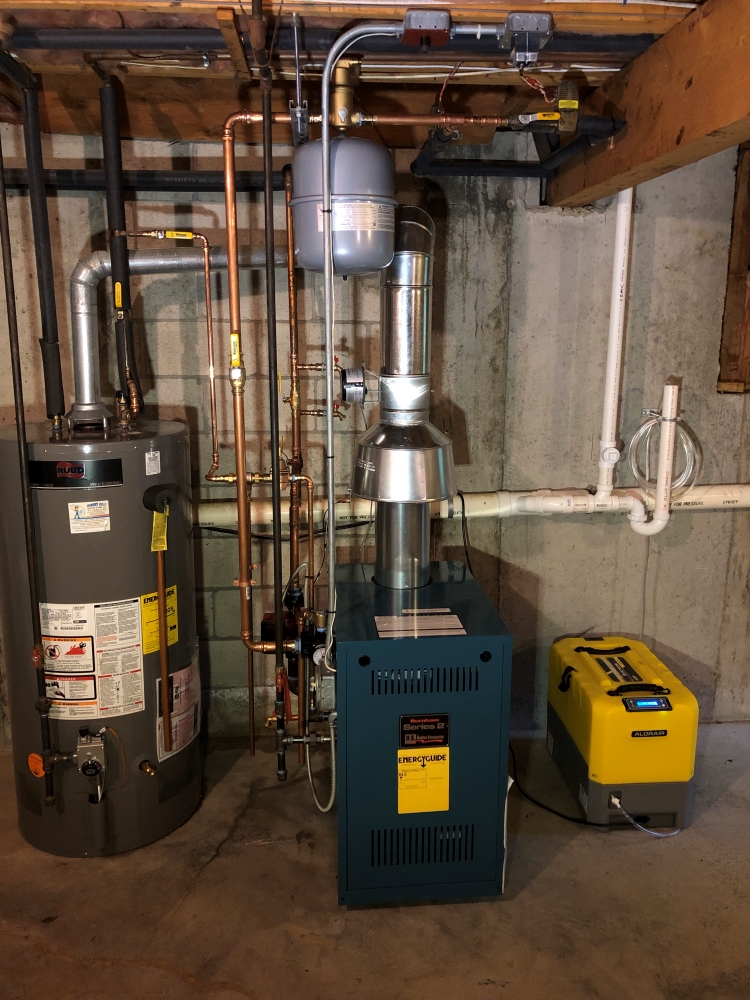
- Boilers: This type of heating system works similarly to a furnace, but uses hot water or steam to generate heat for your home and uses a pump instead of ductwork to circulate hot water through pipes to radiators.

- Heat pumps: In the winter, these systems use electricity to extract heat from the air outside your home and transfer it inside. They do the opposite in summer. There are also geo-thermal heat pumps which use heat from a ground source.

You might also have a secondary heat source.
- Woodstove or Pellet Stove: These are often used in combination with one of the primary heat sources as a way of saving money.
- Wood burning or gas fireplace: Because fireplaces are often not an effective source of heat, these are mostly for ambiance and décor.
- Electric baseboard or space heaters: These convert electric current directly into heat. While easy and cheap to install they are generally very costly to use.
Identification Tips
It’s very important for homeowners to know what kind of heating system they have. Here’s a breakdown of how a client can identify their heating system:
- General Identification Tips:
- Visual Inspection: Start by locating the main heating unit.
- Check the Thermostat: Some thermostats may indicate the type of heating system.
- Observe Air Vents and Radiators: If the home has air vents, it likely has a forced-air system. If the home has radiators or baseboard heaters, it likely has a boiler system.
- Fuel Source: Determine the fuel source.
- Outdoor Units: If there’s an outdoor unit, it could be an air conditioner or a heat pump.
- Documentation: Home inspection reports, previous homeowner’s records, or maintenance records may contain information about the heating system.
- Specific System Identification:
- Furnaces: These systems use forced air through ducts.
- Boilers: These systems heat water, which is then circulated through radiators or baseboard heaters.
- Heat Pumps: These systems transfer heat between the inside and outside of the home.
- Wood/Pellet Stoves: These are freestanding units that burn wood or pellets.
- Electric Baseboard Heaters: These are long, thin units installed along the baseboards of walls.
- When in Doubt, Call a Professional: If a client is still unsure about their heating system, they should contact a qualified HVAC technician.
Conclusion
Understanding your home’s heating system is essential for both safety and insurance purposes. Knowing the type of system you have, its fuel source, and its maintenance requirements can help you protect your property and ensure you have the right insurance coverage.
